Oak
Roble (Quercus humboldtii)
It is also known as Colombian Oak or Andean Oak. Quercus humboldtii is a species belonging to the Fagaceae family, it is distributed in the altitude range between 1400 masl and 3300 masl, in the departments of Antioquia, Boyacá, Caldas, Caquetá, Cauca, Chocó, Cundinamarca, Huila, Meta, Nariño, Quindío, Risaralda, Santander, Tolima, Valle (UNAL, 2022).
Descripción
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPECIES
Large tree that can reach up to 25 m in height. It has simple, alternate, elongated leaves with pointed apex, slightly pubescent, dark green. The flowers are quite small, light yellow, fruits commonly known as acorns which are 50 to 70 mm long and are located on a scaly dome.
ECOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE
This species has been widely exploited for the excellent quality of its wood, which is why its populations have been reduced and currently, according to the IUCN red list, it is in the VU (Vulnerable) category. Based on the above, it is important to plant this species rigorously, since the ecosystems of the Robledal are of great importance for the vegetal structure of the mountain ranges in the country.
ASSOCIATED FAUNA IN THE AREA
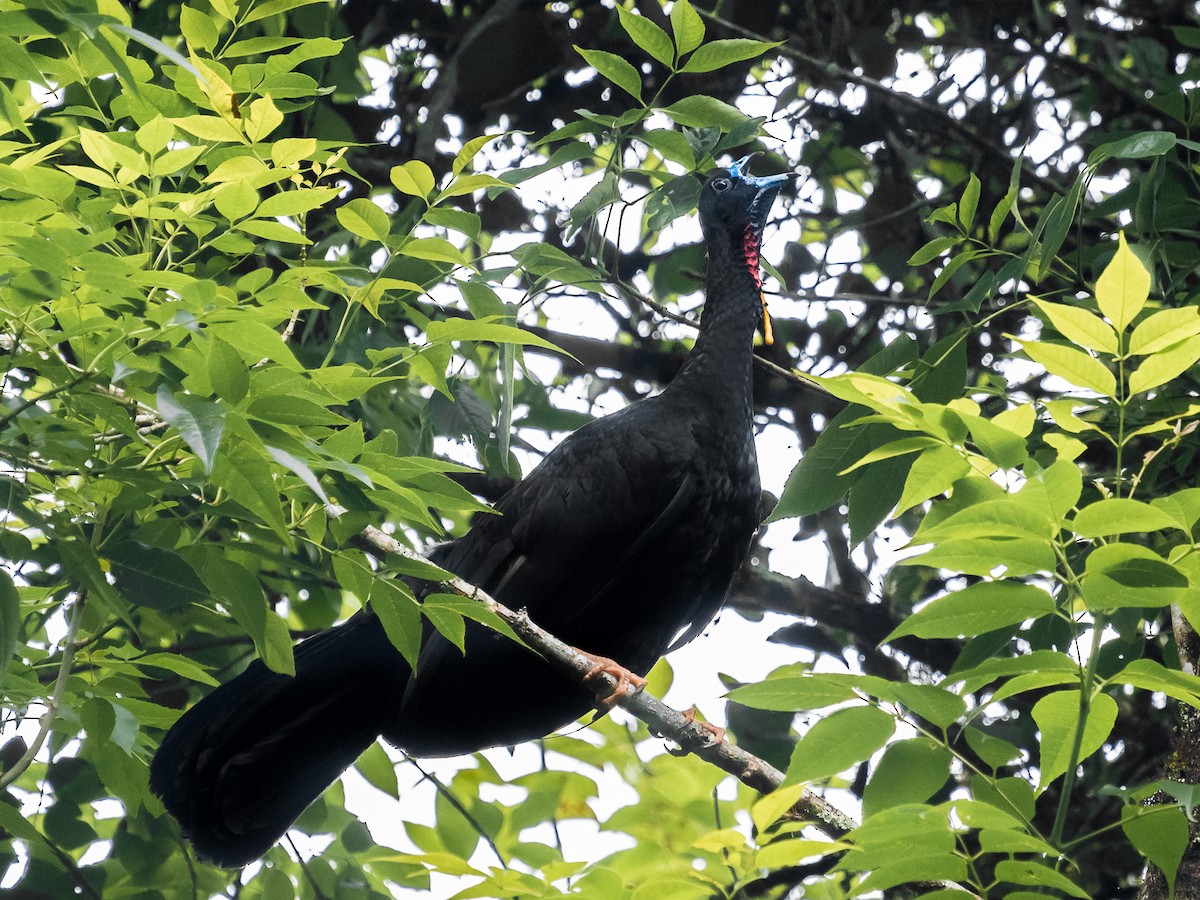
The importance of Quercus humboldtii not only lies in the fact that the species itself is in a certain degree of threat, in addition to this it also provides shelter and food to a bird that according to the IUCN red list is Near Threatened (NT): the boring turkey ( Aburria bordi). The main threat that this bird faces is precisely deforestation, one more reason to plant Oak, to return species such as the bored Guan to their habitat (ICESI, 2016).

 Mother of Water
Mother of Water  Slip Monkey
Slip Monkey  Mortiño
Mortiño  Sangregado
Sangregado 





 Fundación
Fundación